Carrying too much or too little weight can increase a person’s risk of health problems, either now or in the future.
A person’s BMI is not the only factor that affects this risk. Other body composition tools for determining whether or not a person is at a healthy weight include waist-to-hip ratio, waist-to-height ratio, and body fat percentage.
However, BMI is a useful starting point. This article provides some tools for people to work on their BMI.
BMI Calculators
These calculators and charts can indicate whether or not a person’s weight may affect their risk of health problems.
This article is published by The Calculator courtesy of The Calculator Site. Two calculation options are available: metric and imperial.
Calculate your Body Mass Index
This BMI calculator is for informational purposes only. Consult a healthcare provider before making health decisions. BMI is an indirect assessment of health risk and may not be accurate because it cannot determine the proportion or distribution of body fat.
BMI Charts
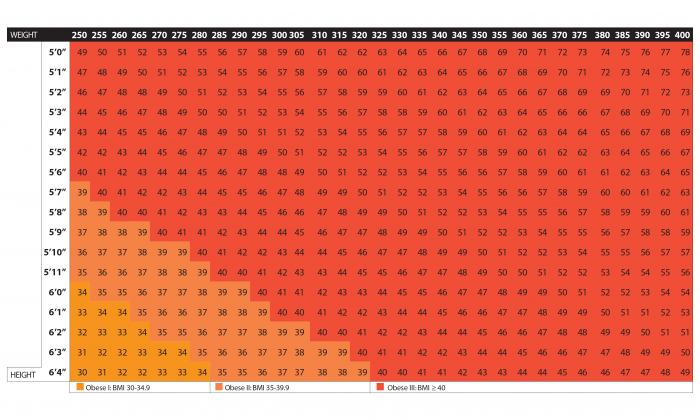
To use the charts below, one can look at their weight in pounds from the top and their height in feet and inches from the bottom. They can then look around to find their BMI.
There are two charts. If a person weighs 245 pounds (lb) or less, they should use the first chart. If they weigh more than 250 pounds, they should see another.
Shaded areas correspond to BMI values that indicate either moderate weight, overweight or obesity.
In addition, researchers and doctors have divided obesity into three categories:
- Class 1: BMI is 30–34.9.
- Class 2: BMI is 35–39.9.
- Class 3: BMI is 40 and above.
The charts are an adaptation of the adult BMI chart created by the University of Vermont in Burlington.
BMI chart: Weight of 95–245 lb

BMI chart: Weight of 250–400 lb
These figures are a guide only. BMI tools do not determine whether a person’s body weight is ideal, but they can help show whether a person’s weight may increase their risk of disease.
A person who is very fit, such as an Olympic athlete, may have a high BMI. However, this does not necessarily mean that they are overweight due to excess body fat. Excess weight, in this case, can be caused by an increase in muscle mass.
BMI Categories
The following table shows the standard weight status categories associated with BMI ranges for adults:
| Below 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5–24.9 | Healthy |
| 25–29.9 | Overweight |
| 30 and above | Obese |
A BMI of less than 18.5
A BMI of less than 18.5 indicates that a person is underweight, so they may need to gain some weight. They should ask a doctor or nutritionist for advice.
BMI of 18.5 – 24.9
A BMI of 18.5–24.9 indicates that a person is at a healthy weight for their height. By maintaining a healthy weight, they can reduce their risk of developing serious health problems.
BMI of 25 – 29.9
A BMI of 25-29.9 indicates that a person is slightly overweight. A doctor may advise them to lose some weight for health reasons. They should talk to a doctor or nutritionist for advice.
BMI of over 30
A BMI of more than 30 indicates that a person is obese. If they do not lose weight, their health may be at risk. They should talk to a doctor or nutritionist for advice.
Health Risks
Maintaining a moderate weight can help prevent various health conditions.
People who are overweight have a higher risk of conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, sleep deprivation, and colorectal cancer. Some of them can be fatal.
Being underweight can increase the risk of malnutrition, osteoporosis, anemia and a number of other problems that can result from a lack of various nutrients. It can also be a sign of hormonal, digestive or other problems.